Find some editors in the list which also support TeX and LaTeX to help you insert. It gives you the ease of writing in markdown language without any. Nearly all Markdown applications support the basic syntax outlined in John Gruber’s original design document. There are minor variations and discrepancies between Markdown processors — those are noted inline wherever possible. To create a heading, add number signs (#) in front of a word or phrase. The number of number signs you.
- Markdown Language Support
- Markdown Language Support Free
- Markdown Language Support Group
- Github Markdown Language Support
'EViews 12 raises the ante with a new workfile format…'
Version 12 improves upon the tried-and-trusted EViews interface and programming language with the following new features:
New File Format
The EViews file format, the workfile .wf1 file, is an efficient and robust format that has not changed since EViews 1! In fact you can take a workfile created in EViews 12, and open it in EViews 1, and vice-versa. One of the downsides of the EViews .wf1 file format is that it is a closed format - only EViews is able to open, edit or create .wf1 files.
EViews 12 introduces a brand new, file format, .wf2. This new format is based upon the open JSON standard, and is both human-readable and can be opened/edited/created by external applications.
The .wf2 file format is optional, and the old .wf1 will still be available permanently allowing backwards compatibility.
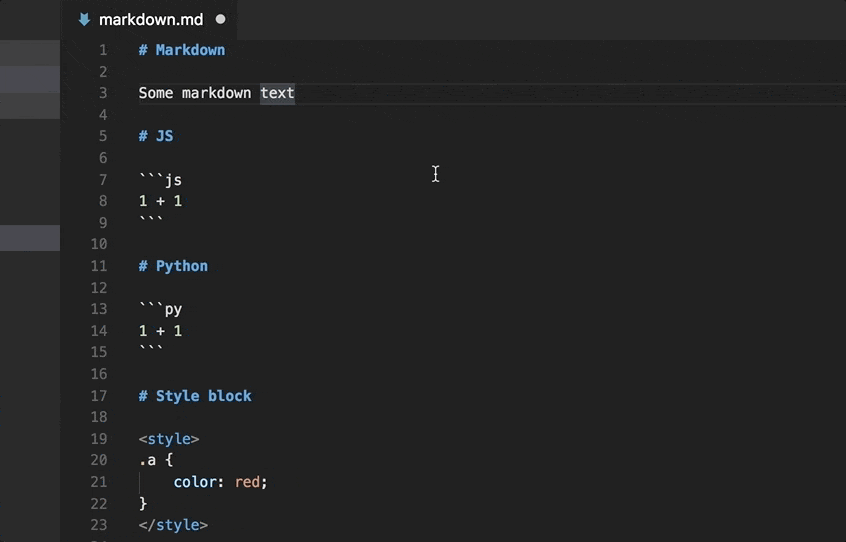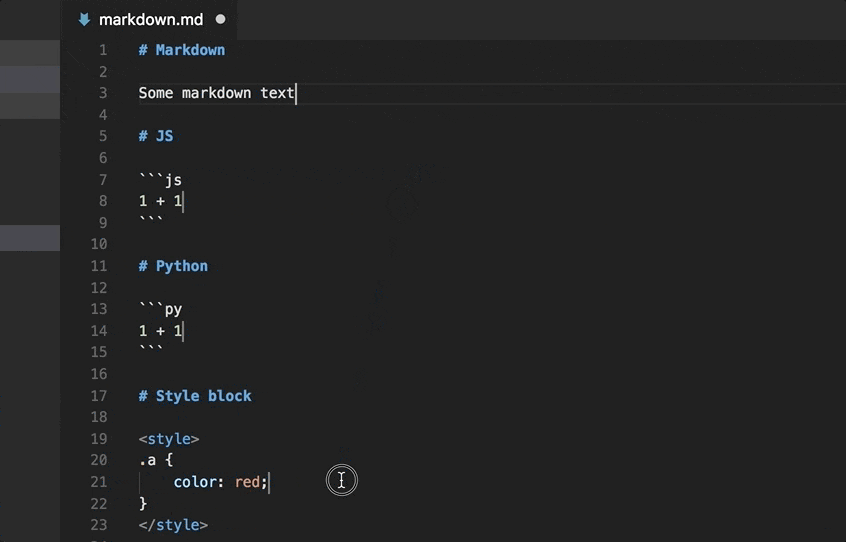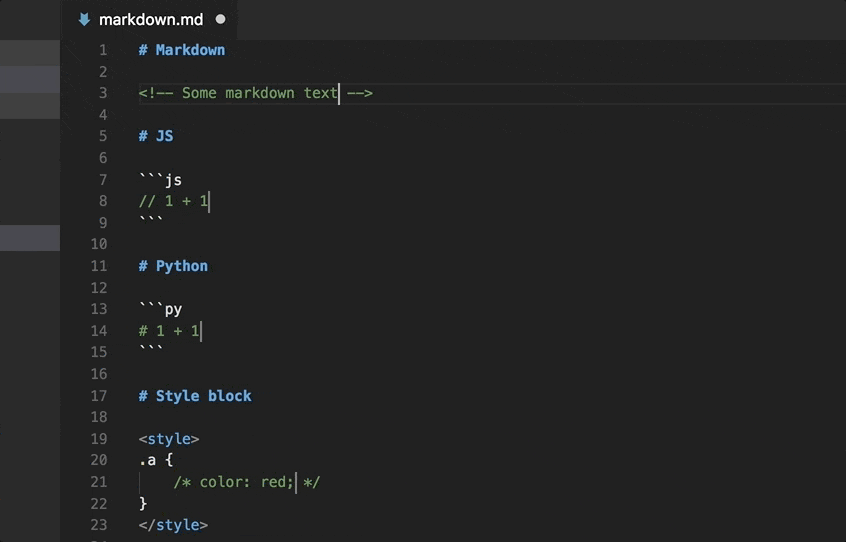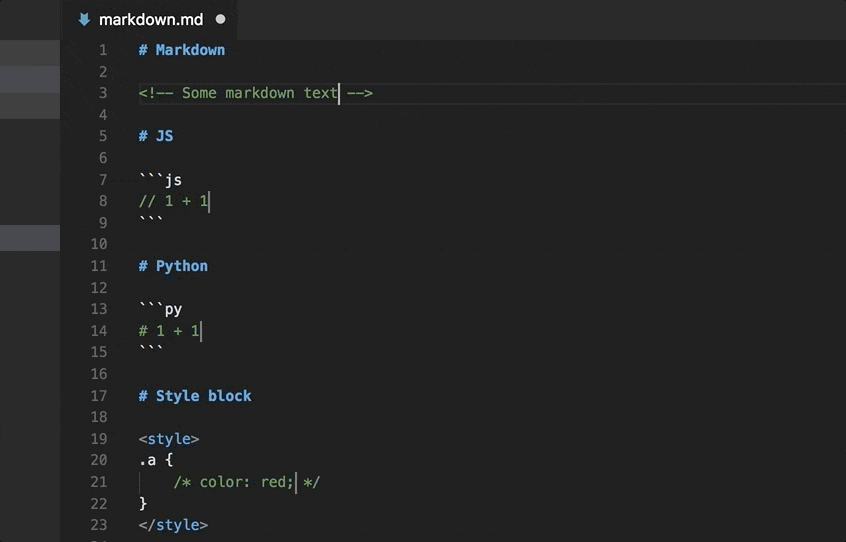
Markdown Language Support
EViews 12 has extended the printing capabilities of EViews with Markdown. Tables, graphs, and other output objects can now be formatted with the basic features of this simple, easyto-read markup language.
Miscellaneous Improvements
EViews 12 also includes miscellaneous other interface improvements:
- Improved Python support.
- Various new functions.
- Color printing of programs.
- Matrix based least-squares calculations.
Hundreds of programming languages supported
In Visual Studio Code, we have support for almost every major programming language. Several ship in the box, for example, JavaScript, TypeScript, CSS, and HTML but more rich language extensions can be found in the VS Code Marketplace.
Here are eight of the most popular language extensions:
Go to the Marketplace or use our integrated extension manager and search for your desired programming language to find snippets, code completion/IntelliSense providers, linters, debuggers and more.
Note: If you want to change the display language of VS Code (for example, to Chinese), see the Display Language topic.
Language specific documentation
Learn about programming languages supported by VS Code. These include: C++ - C# - CSS - Dart - Dockerfile - F# - Go - HTML - Java - JavaScript - JSON - Less - Markdown - PHP - PowerShell - Python - SCSS - T-SQL - TypeScript.
Click on any linked item to get an overview of how to use VS Code in the context of that language. Most language extensions also contain a summary of their core features in their README.
Language features in VS Code
The richness of support varies across the different languages and their extensions:
- Syntax highlighting and bracket matching
- Smart completions (IntelliSense)
- Linting and corrections
- Code navigation (Go to Definition, Find All References)
- Debugging
- Refactoring
Changing the language for the selected file
In VS Code, we default the language support for a file based on its filename extension. However, at times you may wish to change language modes, to do this click on the language indicator - which is located on the right hand of the Status Bar. This will bring up the Select Language Mode dropdown where you can select another language for the current file.
Tip: You can get the same dropdown by running the Change Language Mode command (⌘K M (Windows, Linux Ctrl+K M)).
Language Id
VS Code associates a language mode with a specific language identifier so that various VS Code features can be enabled based on the current language mode.
A language identifier is often (but not always) the lowercased programming language name. Note that casing matters for exact identifier matching ('Markdown' != 'markdown'). Unknown language files have the language identifier plaintext.
You can see the list of currently installed languages and their identifiers in the Change Language Mode (⌘K M (Windows, Linux Ctrl+K M)) dropdown.
You can find a list of known identifiers in the language identifier reference.
Adding a file extension to a language
You can add new file extensions to an existing language with the files.associationssetting.
For example, the setting below adds the .myphp file extension to the php language identifier:
IntelliSense (⌃Space (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Space)) will show you the available language identifiers.
Next steps
Now you know that VS Code has support for the languages you care about. Read on...
- Code Navigation - Peek and Go to Definition and more
- Debugging - This is where VS Code really shines
Common questions
Can I contribute my own language service?
Yes you can! Check out the example language server in the VS Code Extension API documentation.
What if I don't want to create a full language service, can I reuse existing TextMate bundles?
Yes, you can also add support for your favorite language through TextMate colorizers. See the Syntax Highlight Guide in the Extension API section to learn how to integrate TextMate .tmLanguage syntax files into VS Code.
Can I map additional file extensions to a language?
Markdown Language Support
Yes, with the files.associationssetting you can map file extensions to an existing language either globally or per workspace.
Here is an example that will associate more file extensions to the PHP language:
Markdown Language Support Free
You can also configure full file paths to languages if needed. The following example associates all files in a folder somefolder to PHP:
Note that the pattern is a glob pattern that will match on the full path of the file if it contains a / and will match on the file name otherwise.
How do I set the default language for new files?
Using the files.defaultLanguagesetting, you can map all new files to a default language. Whenever a new blank file is opened, the editor will be configured for that language mode.
Markdown Language Support Group
This example will associate new files with the HTML language:
Github Markdown Language Support
